How to Choose the Right Strain Wave Gear for Your Robotics Applications
In the field of robotics, the selection of the right strain wave gear is critical for optimizing performance and ensuring the longevity of systems. As highlighted in a report by the Robotics Industries Association, the global robotics market is projected to grow to $210 billion by 2025, presenting ample opportunities for leveraging advanced components such as strain wave gears, which offer high torque density and compact size. This makes them a favorite in applications ranging from robotic arms to precision medical devices.
Expert insights emphasize the importance of this component choice. According to Dr. Emily Thompson, a leading authority in motion control systems, “The effectiveness of robotic systems heavily relies on the precision and reliability of strain wave gears. Choosing the right configuration can significantly enhance both performance and efficiency.” With her expertise, it becomes evident that selecting the appropriate strain wave gear not only influences the mechanical capabilities but also impacts the overall system design, which is crucial for achieving desired operational goals.
As robotic technologies continue to evolve, understanding the specific requirements of your application becomes essential when choosing strain wave gears. This entails careful consideration of parameters such as load capacity, reduction ratio, and backlash, ensuring that each choice aligns with the intended use and performance criteria. By following these guidelines, engineers can significantly enhance the functionality and durability of their robotic solutions.

Understanding Strain Wave Gears: Definition and Functionality
Strain wave gears, also known as harmonic drive gears, are a unique solution in the field of robotics, characterized by their high reduction ratios and compact design. Defined by their distinctive three-part structure consisting of a flexible spline, a rigid spline, and a wave generator, these gears function through the application of an elliptical motion that enables smooth torque transmission. According to a recent market analysis by Allied Market Research, the global harmonic drive market is projected to reach USD 1.8 billion by 2027, driven largely by advancements in robotics and automation technologies.
The functionality of strain wave gears provides substantial advantages in precision applications, such as robotic manipulators and actuators, where accuracy and size constraints are critical. These gears have demonstrated an impressive ability to maintain high torque while minimizing backlash—often less than 1 arc minute—making them ideal for high-performance robotic systems. Additionally, their lightweight and compact configuration makes them attractive for applications where space and weight are limiting factors. The ongoing integration of strain wave gears in fields such as aerospace, medical devices, and manufacturing is a testament to their growing significance in modern robotics applications, underscoring the importance of understanding their unique characteristics for optimal selection.
Strain Wave Gear Performance Analysis
This bar chart illustrates the torque capacity, efficiency, and backlash of different types of strain wave gears suitable for robotics applications. The values are based on typical performance metrics observed in the field.
Key Performance Metrics: Torque, Ratio, and Efficiency in Robotics
When selecting a strain wave gear for robotics applications, key performance metrics such as torque, ratio, and efficiency are crucial considerations. Torque determines the load-carrying capacity of the gear system, which plays a significant role in ensuring that robotic components can perform their intended tasks effectively. High torque is needed for applications requiring significant force, such as robotic arms or heavy-duty machinery, where the ability to manipulate or lift objects is paramount. Therefore, understanding the torque specifications of a strain wave gear enables engineers to match the gear to the demands of their specific robotic applications.
The gear ratio is another vital metric that influences the overall performance of a robotic system. It dictates how much the input motion translates into output motion, affecting speed and precision. A favorable gear ratio allows for fine adjustments in motion control, which is particularly important in tasks like assembly, inspection, or precise manipulation. Moreover, a higher gear ratio can provide increased torque under certain conditions, making it essential to balance the required speed and torque according to the application's demands.
Efficiency is the final metric to consider, as it reflects how effectively the gear transmits power from one component to another. High efficiency minimizes energy losses within the system, reducing thermal losses and prolonging the lifespan of both the gear and the entire robotic assembly. In demanding applications where energy consumption is a concern, achieving a higher efficiency rating can lead to significant operational cost savings and more sustainable practices. Therefore, when choosing a strain wave gear, it's essential to evaluate each of these metrics comprehensively to ensure optimal performance in robotic applications.
How to Choose the Right Strain Wave Gear for Your Robotics Applications - Key Performance Metrics
| Strain Wave Gear Type |
Torque (Nm) |
Gear Ratio |
Efficiency (%) |
Weight (kg) |
| Type A |
20 |
100:1 |
92 |
1.2 |
| Type B |
25 |
50:1 |
90 |
1.5 |
| Type C |
15 |
80:1 |
88 |
1.0 |
| Type D |
30 |
120:1 |
91 |
1.8 |
| Type E |
22 |
60:1 |
89 |
1.4 |
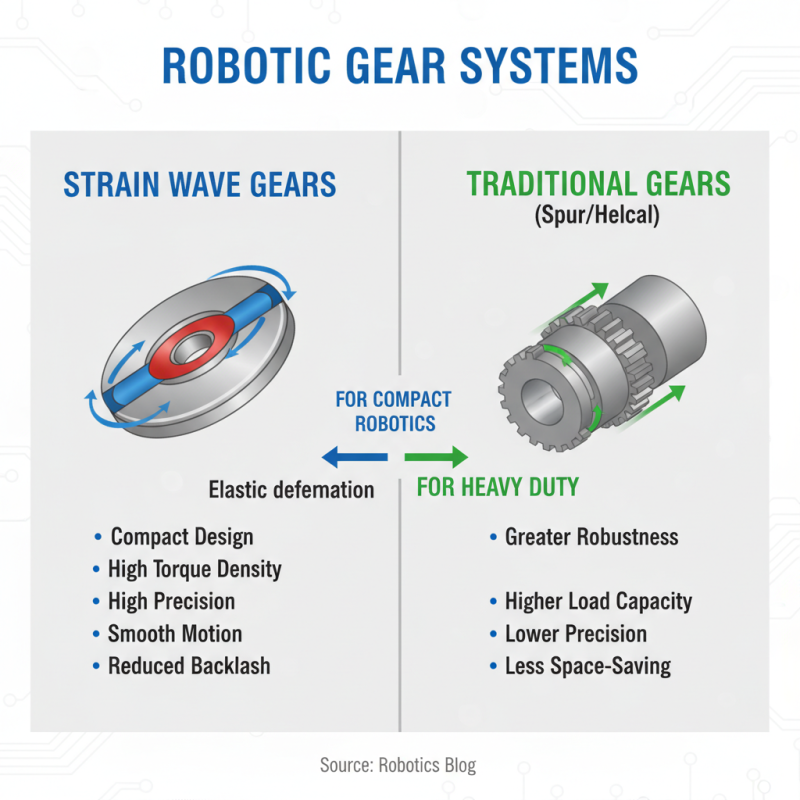
Comparative Analysis: Strain Wave Gears vs. Traditional Gearing Solutions
When selecting gear systems for robotics applications, one critical decision is the choice between strain wave gears and traditional gearing solutions. Strain wave gears, often praised for their compactness and high torque density, leverage the unique properties of elastic deformation to achieve high precision. This allows for smoother motion and reduced backlash, which are crucial in intricate robotic tasks. In contrast, traditional gearing solutions, such as spur or helical gears, may offer greater robustness at higher load capacities but can fall short in the precision and space-saving categories, making them less ideal for compact robotic systems.
Furthermore, the manufacturing process of strain wave gears allows for more intricate designs without the need for extensive additional components, thus reducing assembly times and potential points of failure. On the other hand, traditional gears often involve numerous parts that can complicate maintenance and repair. While they are typically easier and cheaper to produce, the trade-offs in performance, such as increased weight and lower efficiency in some scenarios, can be a significant drawback for advanced robotics applications. Ultimately, the choice between these two technologies should be guided by specific application requirements, including space constraints, load demands, and the need for precision.
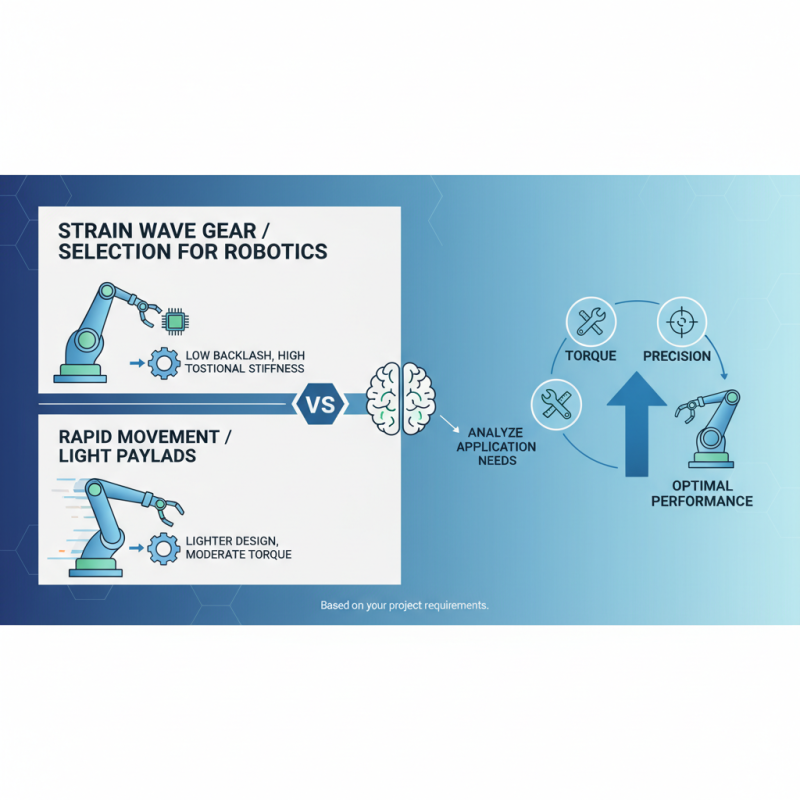
Selecting the Right Strain Wave Gear: Application-Specific Considerations
When selecting a strain wave gear for robotics applications, it's essential to consider the specific requirements of your project. Different applications demand varying levels of torque, size, and precision. For instance, robotic arms that require high accuracy for delicate tasks will benefit from a gear with lower backlash and enhanced torsional stiffness. In contrast, applications necessitating rapid movement may prioritize a lighter design, even if it sacrifices some torque handling capacity. Analyzing your application's purpose and constraints will guide you towards the appropriate strain wave gear.
**Tips:** Always evaluate the load conditions your robot will encounter. Measure the maximum torque requirements and ensure that the strain wave gear can handle this without compromising performance. Additionally, consider the gear's weight and size relative to the robotic design, as excess weight could impair your system's efficiency.
Moreover, the environment in which the robotics application will operate is a vital consideration. Factors such as operating temperature, exposure to dust or moisture, and potential corrosive elements can greatly affect gear performance and longevity. Selecting a strain wave gear made from materials suited to your operational environment can significantly enhance durability and reduce the frequency of maintenance interventions.
**Tips:** Conduct thorough testing in real-world conditions to observe how your chosen gear properties affect overall performance. This ensures that you make informed decisions based on empirical data rather than theoretical assumptions.
Future Trends: Innovations and Advancements in Strain Wave Gear Technology
The future of strain wave gear technology is set to transform robotics applications, driven by innovations that enhance performance, efficiency, and adaptability. Recent advancements focus on improving the precision and load capacity of strain wave gears, making them ideal for increasingly demanding robotics tasks, such as in automation and artificial intelligence integration. Engineers are exploring new materials and designs that not only reduce weight but also increase durability, ultimately leading to more compact and reliable robotic systems. These developments pave the way for more sophisticated robotic solutions capable of operating in diverse environments.
Moreover, the trend toward smart manufacturing and the Internet of Things (IoT) is influencing strain wave gear technology. Innovations in sensors and data analytics allow for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, which can significantly enhance the lifecycle and efficiency of robotic systems. As industries increasingly embrace automation, the demand for strain wave gears that can seamlessly integrate with intelligent control systems continues to rise. This intersection of gear technology with digital advancements promises to revolutionize how robots interact with their environments, leading to enhanced functionality and versatility across various applications.