What is a Gear Reducer and How Does it Improve Mechanical Efficiency
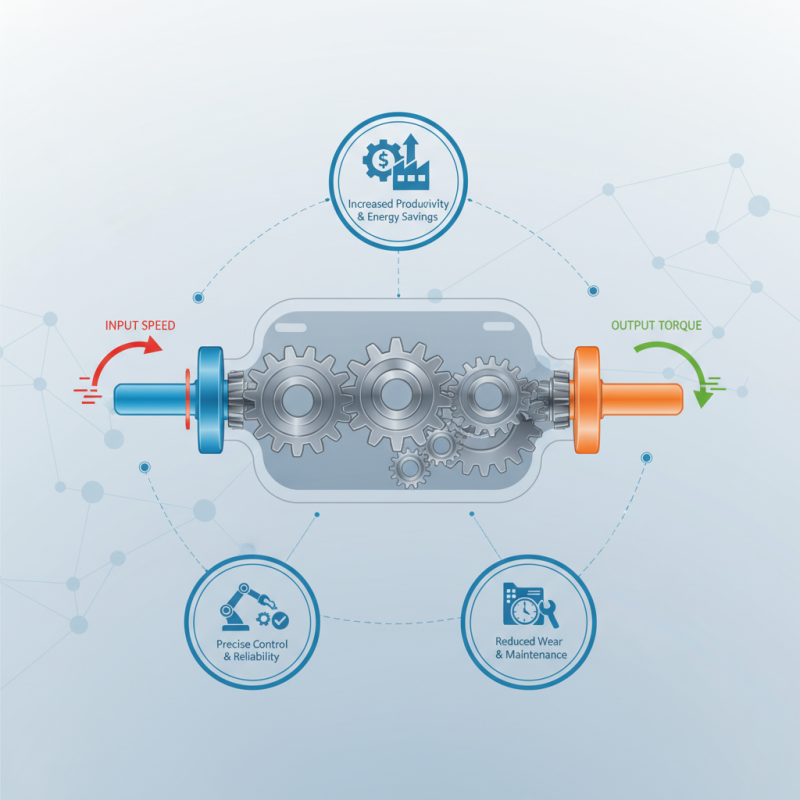
In the realm of mechanical engineering, gear reducers play a pivotal role in enhancing the performance and efficiency of machines. By reducing the speed of an input shaft while simultaneously increasing torque output, gear reducers enable systems to operate more effectively under varying loads and conditions. This dynamic adjustment not only improves the reliability of machinery but also contributes to energy savings, reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
As industries strive for higher productivity and efficiency, understanding the mechanics behind gear reducers becomes crucial. These devices find applications across a multitude of sectors, from manufacturing to robotics, where precise control of speed and power is essential. The adoption of gear reducers allows for the optimization of equipment performance, ensuring that machines can handle demanding tasks with reduced wear and tear, ultimately leading to longer lifespans and lower maintenance requirements.
This exploration of gear reducers will delve into their operating principles, benefits, and the ways they integrate into various mechanical systems, illuminating their indispensable role in modern engineering and industrial processes.
What is a Gear Reducer: Definition and Key Components
A gear reducer, also known as a gear reduction unit, is a mechanical device that decreases the speed of a motor output while increasing the torque. At its core, a gear reducer incorporates essential components such as gears, bearings, and housing. Understanding these key components is crucial for optimizing performance in industrial applications. For instance, gear teeth, which can be spur, helical, or bevel, play a vital role in ensuring smooth power transmission while reducing wear and stress on the system.
According to the Research and Markets report, the global gear reducer market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 4.2% from 2021 to 2026. This growth highlights the increasing demand for energy efficiency in various fields, such as manufacturing, automotive, and robotics. The greater the reduction ratio, the more efficient the application; high-quality gear reducers can achieve efficiency ratings exceeding 95%.
Tips: When selecting a gear reducer, consider factors like the application requirements, load capacity, and input/output speed ratios. Regular maintenance checks can also significantly extend the lifespan of a gear reducer, ensuring consistent efficiency and reliability in performance. Additionally, evaluating the compatibility of the gear reducer with existing machinery can prevent costly downtimes and improve overall systems integration.
Types of Gear Reducers and Their Applications in Industry
Gear reducers are essential mechanical components used widely in various industrial applications to enhance performance by reducing speed while increasing torque. There are several types of gear reducers, each tailored for specific operational needs. The most common types include spur gear reducers, helical gear reducers, bevel gear reducers, and worm gear reducers.
Spur gear reducers are ideal for simple, straightforward applications due to their high efficiency and ease of manufacturing. Helical gear reducers, with their angled teeth, offer smoother operation and are often used in applications where noise reduction is necessary. Bevel gear reducers, on the other hand, are particularly useful in scenarios where the drive shaft needs to be redirected, making them suitable for compact assemblies. Worm gear reducers provide high torque output and are often utilized in heavy-duty machinery due to their self-locking features.
Tips: When selecting a gear reducer, consider the required speed reduction ratio and torque requirements of your application. Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure optimal performance and longevity of these components. Moreover, understanding the specific applications of each type can significantly improve the efficiency of your mechanical systems.
Mechanisms of Gear Reduction: Torque Amplification and Speed Reduction
Gear reducers play a crucial role in mechanical systems by allowing for effective torque amplification and speed reduction. The fundamental mechanism behind gear reduction involves a system of gears with varying sizes, where a smaller gear drives a larger gear. This setup enhances torque, meaning that the output shaft can deliver greater force than the input shaft, making it an essential component in applications requiring high power output with limited input power. The ability to amplify torque enables machinery to perform more demanding tasks that would otherwise require significantly larger input forces.
In addition to torque amplification, gear reducers effectively decrease rotational speed. When the smaller gear rotates at a higher speed, the larger gear will turn more slowly while still maintaining the same amount of work performed. This speed reduction is invaluable in scenarios where high-speed motors need to operate machinery at lower speeds for optimal performance and safety. By adjusting the gear ratio, manufacturers can customize the balance between torque and speed to suit specific applications, thereby achieving improved mechanical efficiency and enabling smoother operation across a variety of tasks.
Impact of Gear Reducers on Mechanical Efficiency and Energy Savings
Gear reducers play a crucial role in enhancing mechanical efficiency by reducing the speed of a motor while increasing torque. When mechanical systems need to operate under heavy loads or specific speed requirements, gear reducers provide an elegant solution by allowing motors to perform optimally without excessive energy consumption. By adjusting the output speed and torque, these devices ensure that machines work more efficiently, leading to significant energy savings over time.
Tips for maximizing energy savings with gear reducers include regularly maintaining the reducer to prevent wear and tear, which can reduce efficiency. Additionally, consider the application requirements and select the appropriate gear ratio to match the load demands closely. This precision helps in minimizing energy loss and optimizing operational performance.
Furthermore, employing gear reducers in conjunction with variable frequency drives (VFDs) can enhance overall system efficiency. VFDs adjust the speed and torque of electric motors, aligning them synergistically with gear reducers for further improvements in energy utilization. This combined approach ensures not only operational effectiveness but also substantial energy reductions in long-term mechanical processes.
What is a Gear Reducer and How Does it Improve Mechanical Efficiency
| Aspect |
Description |
Efficiency Improvement (%) |
Energy Saved (kWh) |
Typical Applications |
| Torque Increase |
Gear reducers amplify motor torque, making it suitable for heavy-load applications. |
15-30 |
500-1500 |
Conveyors, Crushers |
| Speed Reduction |
They reduce speed allowing motors to perform efficiently without overheating. |
10-25 |
300-1200 |
Pumps, Mixers |
| Load Distribution |
They balance the load across multiple gears, enhancing lifespan and reliability. |
5-20 |
200-800 |
Heavy machinery, Wind turbines |
| Noise Reduction |
Designs often minimize vibration and noise produced during operation. |
Improved Effect |
N/A |
Residential applications, HVAC systems |
Industry Statistics: Gear Reducer Performance and Reliability Metrics
The performance and reliability metrics of gear reducers are pivotal in understanding their role in enhancing mechanical efficiency across various industries. Statistics indicate that well-designed gear reducers can improve energy efficiency by reducing friction losses and optimizing torque output. For instance, systems that utilize high-quality materials and precise manufacturing processes often report lower failure rates and longer service life. This reliability translates into reduced downtime and maintenance costs for industrial operations, making gear reducers a vital component in machinery design.
Tips for maximizing the performance of gear reducers include regular maintenance checks and monitoring operational conditions. Ensuring that lubrication is adequate and free of contaminants will maintain optimal gear conditions. Additionally, selecting the appropriate gear reducer size and type based on specific application needs can further enhance both efficiency and reliability. An informed choice, combined with proactive maintenance, will maximize the benefits gained from this critical mechanical component, leading to sustained operational success.








